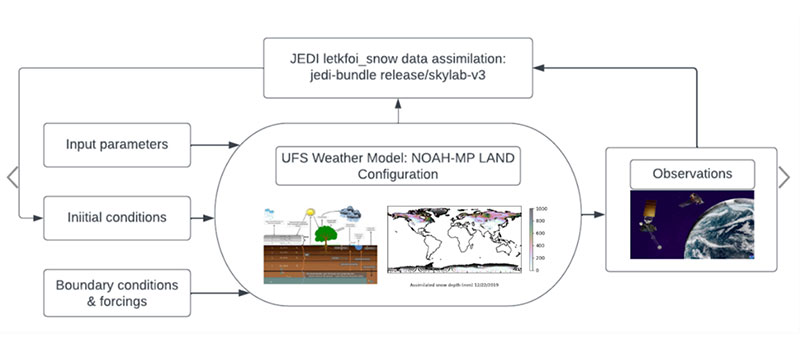
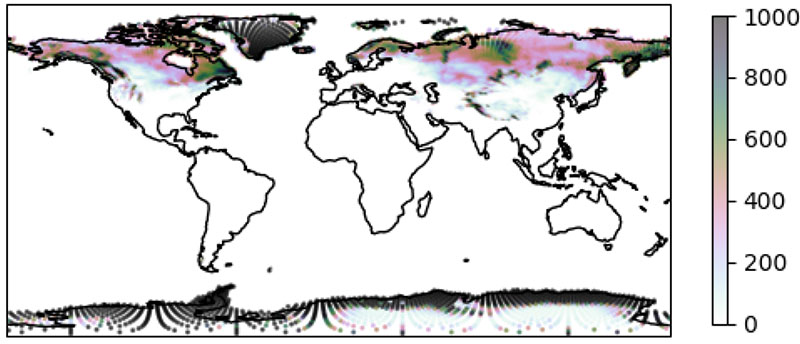
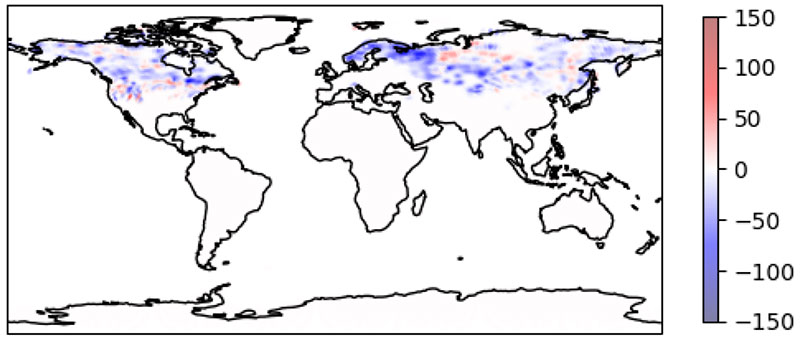
The Earth Prediction Innovation Center (EPIC) and the Unified Forecast System (UFS) community are proud to announce the public release of the UFS Land Data Assimilation (DA) System v1.2.0. This public release v1.2.0 reflects changes currently available in the UFS land-DA_workflow development branch. In the Land DA System, the Noah-MP land surface model (LSM) and the Joint Effort for Data assimilation Integration (JEDI) system are used to assimilate snow depth data via the Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter-Optimal Interpolation (LETKF-OI) algorithm. Key feature updates for this release include:
- Integration of the UFS Noah-MP land component into the Land DA System for use as an alternative to the Common Community Physics Package (CCPP) Noah-MP LSM land driver. The coupling layer of the land component is developed using the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF) and the National Unified Operational Prediction Capability (NUOPC) interoperability layer.
- Updates to model forcing options for use of the UFS land component
- Provided a new analysis option in the cubed-sphere native grid using GSWP3 forcing
- Established global land grid-point consistency with the head of the UFS Weather Model (WM) baseline test cases
- Added a new sample configuration file (settings_DA_cycle_gswp3)
- Included a new ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis forcing option in the existing vector-to-tile conversion analysis process
- CTest suite upgrades—the ERA5 CTests now test the operability of seven major elements of Land DA: vector2tile, create_ens, letkfoi_snowda, apply_jediincr, tile2vector, land_driver, and ufs_datm_land.
- Upgrade of the JEDI DA system to JEDI Skylab v4.0
- Updates to sample datasets for the release (see the Land DA data bucket)
- Singularity container (ubuntu20.04-intel-landda-release-public-v1.2.0.img) updates to support the changes described above
- Documentation updates to reflect the changes for this release
Known issues for this release include:
- For the GSWP3 forcing option, an artificial GHCN snow depth observation file is provided for a single-cycle analysis test for 2000-01-03. The GHCN observation database will be extended in the near future.
While the previous release of the offline stand-alone UFS Land DA System was built on the Noah Multi-Physics (Noah-MP) land surface model (LSM) via the Common Community Physics Package (CCPP), this release applies the Noah-MP model configuration as an external UFS land component. In this framework, the Noah-MP component is configured to run with atmospheric forcing files introduced through the Community Data Models for Earth Prediction Systems (CDEPS). Key state variables simulated by the Noah-MP model are soil moisture (both liquid and frozen), soil temperature, skin temperature, snow depth, snow water equivalent (SWE), snow density, canopy water content, and the energy flux and water flux terms of the surface energy balance and surface water balance.
The UFS Land DA framework uses the Joint Effort for Data assimilation Integration (JEDI) software from the JCSDA Skylab v4.0 release, which includes the Object-Oriented Prediction System (OOPS) for the data assimilation algorithm, the Interface for Observation Data Access (IODA) for observation formatting and processing, and the Unified Forward Operator (UFO) for comparing model forecasts and observations. JEDI applies the Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter-Optimal Interpolation (LETKF-OI) algorithm to combine the state-dependent background error derived from an ensemble forecast with the observations and their corresponding uncertainties to produce an analysis ensemble (Hunt et al., 2007).
An updated v1.2.0 User’s Guide provides further information about the Land DA System and instructions for running and testing the system. Data files required to run Land DA are available to the public in the Land DA data bucket. Interested users can get support by submitting a question through GitHub Discussions.
This continuous Land DA System release is a collaboration between the Earth Prediction Innovation Center (EPIC), the Environmental Modeling Center (EMC), the Physical Sciences Laboratory (PSL), the Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation (JCSDA), and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Climate & Global Dynamics (CGD) Laboratory. It uses the Joint Effort for Data assimilation Integration (JEDI) developed by the JCSDA, the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF) developed by NCAR-CGD, and the CCPP software developed by the Developmental Testbed Center (DTC). Publicly available data is provided via an AWS S3 bucket established as part of the NOAA Open Data Dissemination (NODD) Program. Computing resources used in preparation of this release were provided by NOAA High Performance Computing and Communications (HPCC) Program.
This release was funded by the NOAA Weather Program Office’s EPIC and Joint Technology Transfer Initiative (JTTI) Programs, the National Weather Service (NWS) Office of Science and Technology Integration (OSTI) Modeling Program, and the NOAA Disaster Supplemental Program. The Land Data Assimilation System page may be viewed on the EPIC Community Portal.